 Hyperuricemia, which is commonly known as high uric acid levels, refers to the condition of an excessive amount of uric acid in the blood stream. The clinical ranges for the diagnosis of hyperuricemia are defined as greater than 7mg/dL and 6mg/dL of serum uric acid in men and women, respectively. A high level of uric acid is a common diagnosis, more so in men than in women, and in individuals over 65 years old. However, do you know high uric acid symptoms to help you take note of it? Keep reading to learn more about it.
Hyperuricemia, which is commonly known as high uric acid levels, refers to the condition of an excessive amount of uric acid in the blood stream. The clinical ranges for the diagnosis of hyperuricemia are defined as greater than 7mg/dL and 6mg/dL of serum uric acid in men and women, respectively. A high level of uric acid is a common diagnosis, more so in men than in women, and in individuals over 65 years old. However, do you know high uric acid symptoms to help you take note of it? Keep reading to learn more about it.
Causes of High Uric Acid
The accumulation of uric acid in the blood is linked to either failure to excrete uric acid in urine or increased production of uric acid. Some common causes of high uric acid levels include medical conditions, medications, genetic predisposition, and dietary factors.
- Medications and vitamins: diuretic medications; niacin; vitamin B3; immunosuppressive medications
- Medical conditions: Non-Hodgkin's and Hodgkin's lymphomas; underactive thyroid (Hypothyroidism); Leukemia; Psoriasis; Obesity
- Diet: high levels of caffeine and alcohol consumption; purine-rich foods (meat and meat products, seafood, shell fish, and legumes).
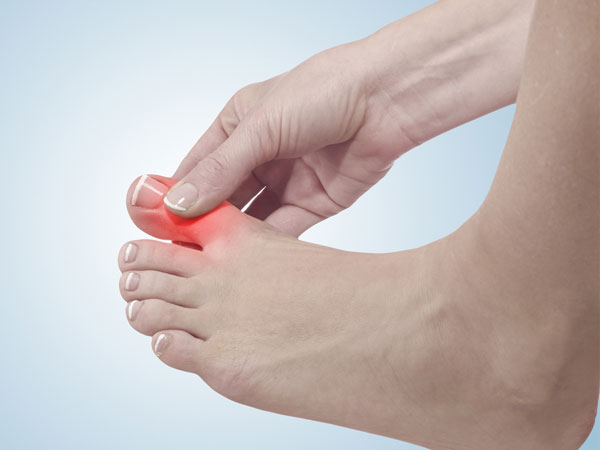
High Uric Acid Symptoms
Increased uric acid levels may go undiagnosed because some people may be asymptomatic. However, some people with high uric acid levels may experience symptoms due to the effects of the excessive uric acid on their bodies. For example, hyperuricemia can lead to gout (inflammation of the joints) and kidney ailments such as kidney stones and kidney failure. These medical conditions are explored in detail below.
- Gout develops due to an immunologic reaction to the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. Gout is characterized by extreme pain in the joint that worsens in response to minimal pressure, inflammation (swelling, warmth, and tenderness) of the joint, fever, and peeling of the skin around the joint. Uric acid levels exceeding 10mg/dL increases the risk of developing gout.
- Kidney stones may develop in people suffering with high uric acid levels, and these kidney stones may go unnoticed until they become stuck in the ureter, causing immense pain, painful and more frequent urination, bloody urine, or nausea and vomiting. Approximately 10% of the kidney stones that are detected in the United States are composed of uric acid. Although uric acid kidney stones are commonly found in gout patients, they are also detected in approximately 20% of patients who have high uric acid levels but not gout. The classic symptoms of kidney stones are sudden and intense pain in the abdomen, flank, and groin region, which tends to come in waves. Additional symptoms include bloody urine and painful urination, and if there is a secondary infection, a fever may be detected.
- Kidney failure. One of the most severe high uric acid symptoms is kidney failure, which manifests as decreased urination, shortness of breath, swelling in the limbs, confusion and drowsiness, fatigue, or chest pain. Kidney failure can develop in patients with leukemia, Hodgkin's lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma due to uric acid levels. This is usually a consequence of chemotherapy, which kills off malignant cells and releases uric acid along with their inner contents.
- Other diseases. Although recent research has suggested that high uric acid levels are linked to hypertension and heart disease, it remains to be determined whether reducing uric acid levels would reverse these conditions.
Treatments for High Uric Acid
If you are diagnosed with hyperuricemia, your doctor will likely advise dietary changes and/or prescribe medications that either treat the underlying disease that may be contributing to the high uric acid levels or that directly regulate the body's metabolism.
- Diet: High uric acid levels can occur as a result of eating a diet that is rich in purines. Therefore, reducing the intake of these foods can lower the high uric acid symptoms. You should avoid foods that are rich in protein and alkaloids, as well as fried foods and white sugar. Interestingly, dietary changes may also be effective in cases of elevated uric acid levels that are unrelated to diet. Eating fruits such as strawberries and drinking black cherry juice may help to lower uric acid levels actually.
- Drug Treatments: In cases of chronic high uric acid levels, the best treatment option is medications that block the body's ability to make or absorb uric acid or enhance the body's ability to excrete uric acid. For example, the drug Probenecid blocks the absorption of urates. On the other hand, the drugs Allupurinol, febuxostate and sulfinpyrazone, block the production of uric acid and/or enhance the excretion of uric acid.
High uric acid levels usually occurs secondary to some other conditions. If an underlying condition is responsible for the high uric acid levels, then remedying that condition is the best treatment strategy. In the event that the underlying condition is untreatable and there is chronic elevation of the uric acid levels, the best treatment option is to target the metabolism of purine.
Notes: Typically, hyperuricemia is uncovered during testing to diagnose some other condition. If high uric acid levels are detected, your doctor may suggest additional tests to better understand your condition and clarify your diagnosis. A better understanding of the underlying conditions that may be contributing to your elevated uric acid levels will help your doctor devise the best treatment regimen. It is important to remember that even if you believe that your current medications may be contributing to your high uric acid levels, you should not stop taking them without consulting your doctor.
