According to the American Cancer Society, this year is going to see more than 36,000 people getting diagnosed with oropharyngeal cancer and mouth cancer, out of which approximately 6,850 will die because of it. Any working part of the mouth can get affected by oral cancer including your gums, teeth, lips, roof of mouth, floor of the mouth located under the tongue, tissue lining your cheeks, lips and throat.
What Does Mouth Cancer Look Like?
Oral cancer is another name given to mouth cancers. Usually dentists diagnose the presence of mouth cancer in people instead of doctors. Excessive drinking, smoking cigarettes, having a member of the family suffering from cancer, chewing of tobacco and severe sun exposure are some of the causes of mouth cancer. The HPV or human papillomavirus has also been found to be responsible for causing oral cancer. It must be remembered that oral cancer can be treated and cured if it is diagnosed at an earlier stage. Thus it is imperative to visit a doctor immediately if you find something wrong with your mouth.
Symptoms of Mouth Cancer
Canker sores are usually the cause of pain in the mouth but they do not last more than two weeks. If you find a bump on roof of mouth or a sore spot that persists for more than two weeks then it becomes necessary to visit the doctor. Besides that, the following are among the symptoms that might indicate the presence of oral cancer.
- Numbness in the mouth, neck or face that you are unable to explain
- Formation of a mass or thickening of the lining or the skin of the mouth
- A patch inside your mouth that is either red or white in color
- Loose teeth
- Dentures that are not fitting properly
- Pain experienced in the tongue
- Stiffness or pain in the jaws
- Inability to chew properly
- Inability to swallow properly
- Sore throat
- Having a feeling that you have something lodged in your throat
- Formation of a mass in the neck. If you find a mass in your neck then it is an indication that the disease has progressed to an advanced stage. It shows that the oral cancer that had been present in the throat or the back of the tongue has metastasized into one of the lymph nodes present in the neck.
What Does It Look Like?
The following are some characteristic features of how mouth cancers look for people wondering what does mouth cancer look like.
- An ulcer that starts bleeding when touched, having rolled edges and a crater in the centre.
- A deep fissure containing a small ulcer
- Erosion of the mucosa resulting in a raw superficial area
- Soft tissues containing a palpable nodule that has become very hard
- Gingival hyperplasia (increase in the size of the gums) affecting a single portion of your mouth
Warning: In the early stage of mouth cancer, it looks exactly like an ulcer. If the sore bump on roof of mouth, patch on tongue, mass formed on gums, swelling or color changes inside the mouth do not go away even after the passage of a few weeks then they should be evaluated by a doctor.
Look Further in Detail
The following are some mouth cancer pictures that can help you in knowing what does mouth cancer look like.
1. Leukoplakia (White and Hardened Patches)
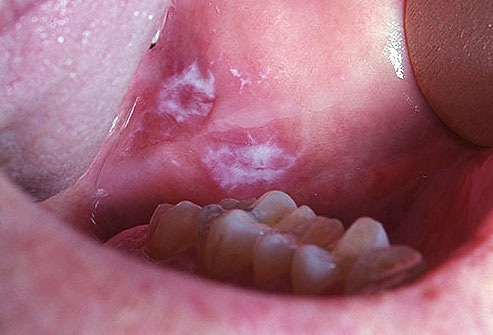
Squamous Cells is the name given to the flat cells that are present on the surface of the tongue, mouth and lips. These cells are the most common grounds for mouth cancers. Seeing a red or white patch on you gums, lining of mouth, tonsil or tongue is a sign of squamous cell carcinoma. The patches having a grayish or white coloring to them present on your lips or inside your mouth are known as Keratosis or Leukoplakia. Although mostly benign, these tissues are abnormal and can get malignant. Scraping these patches is not easy as they are hard and rough. The development of leukoplakia takes time and happens at a slow pace.
This is a picture showing patches of white tissue forming on the underside of the mouth which might be cancerous in nature.
(Picture sourced from Mayo clinic)
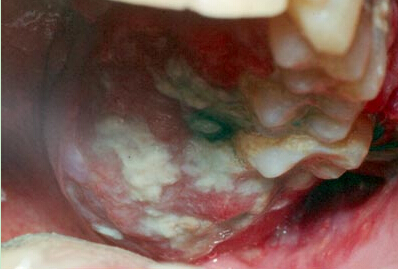
2. Erythroleukoplakia (White and Red Patches)
Erythroleukoplakia is the formation of white and red patches in the mouth. These patches are abnormal cells that have a high chance of becoming malignant. If these patches remain for more than a few weeks then it becomes essential to have it evaluated, notes the American Dental Association. These abnormal patches become visible much earlier than they are felt by the patient because mouth cancer rarely causes any pain in the beginning.
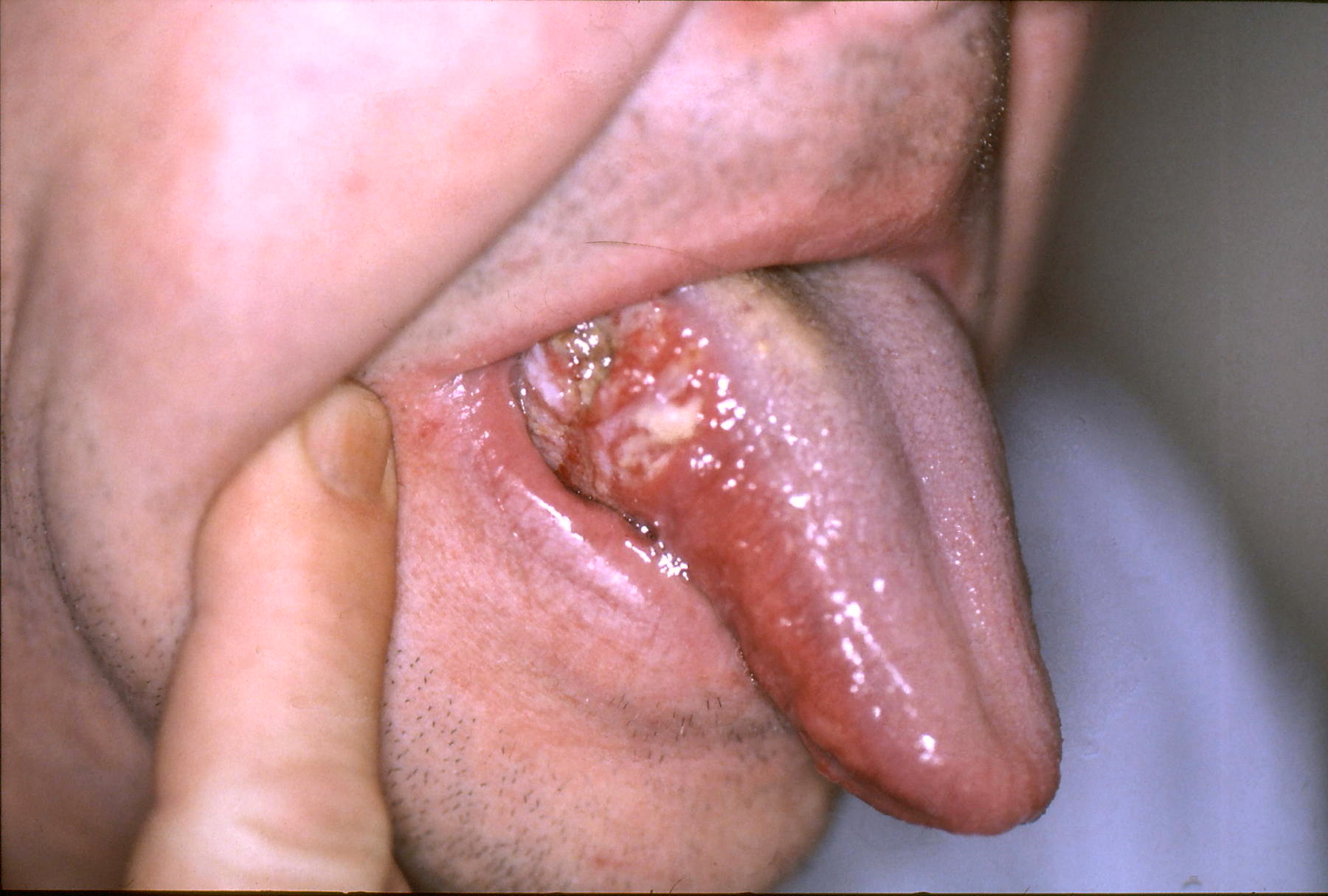
3. Erythroplakia (Red Patches)
Erythroplakia are patches or bright red coloration that form in the mouth and are considered to be cancerous in nature. Since almost 75 to 90% of erythroplakia cases lead to mouth cancers, it is essential that these vividly colored patches are not ignored. Biopsying these cells is a great way of finding out whether they are cancerous or not.
This is a picture of a red sore that has not healed even after the passage of two weeks and can be considered cancerous.
(Picture sourced from Mayo clinic)
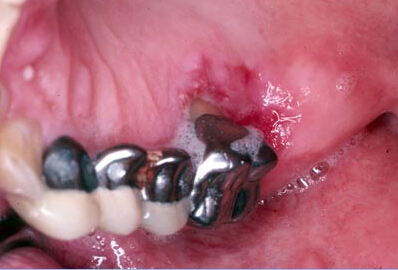
4. Location of Erythroplakia
Although erythroplakia can form anywhere in the mouth, the floor of the mouth located underneath the tongue is where they occur the most. Moreover, the gums present behind your back teeth are also among the locations where erythroplakia are mostly found. You can check for these patches by directing bright light on your mouth and seeing your reflection in a magnifying mirror.
This is a picture showing white patches on the inside portion of the cheeks which are known as leukoplakia and can cause mouth cancer.
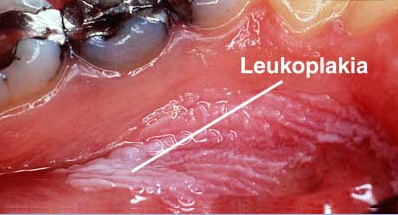
(Picture sourced from Mayo clinic)
This is a picture of a sore appearing on the lip that has shown no signs of healing for two weeks and can be considered cancerous.
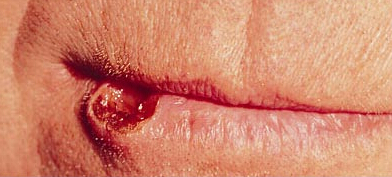
(Picture sourced from Mayo clinic)
How Is Mouth Cancer Diagnosed?
Knowing what does mouth cancer look like is not enough for diagnosis. The following tests and procedures are done to diagnose mouth cancer.
|
Physical Exam |
The dentist is going to inspect your mouth and lips and will look for any sores, lumps, or white patches present inside your cheeks or underneath your tongue. |
|
Tissue Biopsy |
If the dentist finds an area that looks suspicious then he is going to scrape some of the cells present in that area using a brush and send them to the laboratory for a biopsy to determine whether the abnormal cells are cancerous or not. |
|
Further Tests |
Once the diagnosis of mouth cancer has been confirmed, the doctor is going to perform further tests to determine the stage of the cancer. These tests include:
|
Staging Mouth Cancer
The stages of mouth cancer are indicated through roman numerals I to IV with I indicating a lower stage mouth cancer and IV indicating a higher stage mouth cancer. Knowledge of the stage of mouth cancer you are suffering from will help the dentist in deciding which treatment options would work for you.
