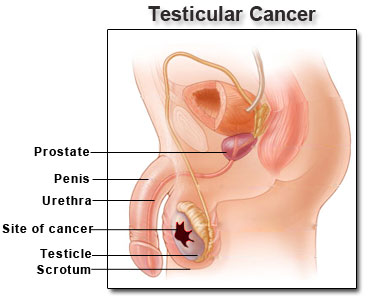
 Testicular cancer is a rare disease that afflicts a lesser population compared to other forms of cancer. The testes is found within the scrotum which is a small bag of skin found under the penis and is responsible for producing hormones and sperm to facilitate reproduction. However, in the US, this is more prevalent especially for males in the age range of 15 to 35. Commonly, one of the very first symptoms of testicular cancer is a sudden formation of lump in the testicles. However, not all lumps on the testicles may be called tumors, and not all tumors, may it be painful or not, are considered as cancerous. A defining characteristic of this deadly disease is not just the presence of lumps accompanied with pain. As many men refuse to see their doctor for their regular check-ups, they are at greater risk of having undetected cancer that spreads fast.
Testicular cancer is a rare disease that afflicts a lesser population compared to other forms of cancer. The testes is found within the scrotum which is a small bag of skin found under the penis and is responsible for producing hormones and sperm to facilitate reproduction. However, in the US, this is more prevalent especially for males in the age range of 15 to 35. Commonly, one of the very first symptoms of testicular cancer is a sudden formation of lump in the testicles. However, not all lumps on the testicles may be called tumors, and not all tumors, may it be painful or not, are considered as cancerous. A defining characteristic of this deadly disease is not just the presence of lumps accompanied with pain. As many men refuse to see their doctor for their regular check-ups, they are at greater risk of having undetected cancer that spreads fast.
What Are The Symptoms of Testicular Cancer?
There are lots of early signs of testicular cancer in men that may help one in preventing it to spread. However, it is possible for testicular cancer to form without any telltale signs.
What Does Testicular Cancer Feel Like?
It can be characterized by intermittent pain in varying intensity in the testicles or scrotum area, a feeling of heaviness and simply not feeling well. One of the most common symptoms of testicular cancer is having an enlarged testicles or a lump on the testicles. These testicular lumps may appear the same size as a pea or a marble, and may even grow larger.
Can the Lump Be Something Else?
Lumps on the testicles, may they be painful or not, does not always automatically mean that you have testicular cancer. It may be a cyst in the epididymis, enlargement of the blood vessels in the testicle, formation or the build-up of the fluid in the testicles’ membrane or maybe an opening in the abdominal muscle. Not all lumps on the testicles are tumors, and not all tumors are malignant (cancerous). Other conditions, like epididymal cysts, testicular microlithiasis, and appendix testis (hydatid of Morgagni), may be painful but are non-cancerous.
Other Symptoms of Testicular Cancer
- Aside from obvious lumps in the testicles, other symptoms of the testicular cancer may include the enlargement of the testicles or a sudden change in how it feels. You may notice it hardening, getting heavier, or have an uneasy feeling of tenderness. Any new sensations in this private and sensitive part must be raised with your doctor so you can undergo tests. This is important to confirm if it really is testicular cancer. The enlargement of your testicles may be alarming, but it is also possible for your testicles to shrink.
- Another symptom of testicular cancer is pain or discomfort. Regardless if there is a lump or none, when you suddenly feel pain or discomfort in your testicle or the scrotum, it would be best to see the doctor. Experiencing pain in your testicles does not always mean that you have testicular cancer as it may also be a symptom of an infection, an injury, or that the testicles were only twisted.
Symptoms of Metastatic Cancer
Are you suffering from lower back pain even though you did not lift anything heavy nor undergo a heavy activity? Smoker or non-smoker, do you feel like it is becoming more often that you are having shortness of breath even though you only walked up one flight of stairs or you only did minimal activity? Do you have phlegm even though you do not have that much of a cold? All these symptoms may sound like they are regular occurrences in life. However, all these may also indicate that your testicular cancer has metastasized or spread to lymph nodes in the abdomen or the lung.
The testicles are affected in the hormones and so are the breasts. Commonly, pain or tenderness in the breasts may be signs of breast cancer (even in men), but it is also one of the signs that testicular cancer has spread. Though you’re a man, do not hesitate to see your doctor whenever you are feeling a sudden tenderness or sensitivity in your breasts.
Cause and Risk Factors of Testicular Cancer
It's not clear what causes testicular cancer in most cases. There are risk factors that may cause or trigger testicular cancer:
- One of them is having undescended testicles. When the baby is being formed in the womb, the baby develops his or her reproductive system. However, there are some babies who fail to develop fully (the testes fail to descend into the scrotum), thus they are the ones who need to undergo a surgery to move the testicles down. This kind of medical condition called cryptorchidism commonly acquires testicular cancer.
- Aside from having undescended testicles, race and age are also some of the factors to look at. Testicular cancer is common to the younger to the middle generation ranging from ages 15-49, and is usually acquired by white men as compared to other ethnic races.
- Also, one of the most natural causes of testicular cancer is the family history. It is important to know and discover if there is anyone in the family who has acquired testicular cancer because a big percentage of those tested positive in this kind of sickness acquired it genetically.
Early Diagnosis of Testicular Cancer
Since one of the first symptoms of testicular cancer is a testicular lump, it would be best to have it checked up with the doctor. There are various ways to confirm if the lump on your testicles is indeed related to cancer.
1. Testicular Ultrasound
First is a testicular ultrasound where sound waves create an image of the scrotum and the testicles. In this diagnosis, you will have to lie down and spread your legs so the doctor can apply a clear gel on your organ. After that, the doctor will use a hand-held probe so as to make an ultrasound of your testicles. With this type of diagnosis, the doctor will be able to find out if the lump is inside or outside the testicles and if it is solid or fluid-filled.
2. Blood Test
Second is a blood test. With blood tests, the doctor will be able to determine the certain level of tumor marks in your blood. Tumor marks are the substances that form in your blood that are caused by testicular cancer.
3. Surgery
Third is the surgery to remove the testicles. The removed testicle will be subject to analysis so the doctors will be able to determine if the testicular lumps are indeed cancerous and what type of cancer is present. There are two types of testicular cancer: seminoma and nonseminoma. Seminoma tumor can occur in all age groups. However, if older men acquire testicular cancer, it is most likely to be this type of cancer. Nonseminoma tumors are considered to be more aggressive than seminoma and there are also various types of this tumor such as choriocarcinoma, teratoma, yolk sac tumor, and embryonal carcinoma.
Stages of Testicular Cancer
Determining the stage of cancer may be done using two procedures: first is a computerized tomography (CT) scan where the doctor takes a series of X-ray images of the pelvis, the chest and the abdomen and second, blood tests so as to decipher if the cancer will remain in the body after the removal of the testicles.
There are three stages of cancer: first stage is when the cancer is limited to the testicle, second is when the cancer already reached the lymph nodes in the abdomen; third, if the cancer has spread into the lymph nodes in the upper part of the body like the lungs and liver.
