 A blood clot in the brain can cause an ischemic stroke which is caused by an artery to the brain becoming blocked and starving a portion of the brain of oxygen and nutrients. A clot in the brain can also cause a buildup of cellular waste and carbon dioxide because the brain will be unable to clear this waste properly. This can cause the cells around the blockage to die, and the neurons in this portion of the brain to stop working, which can cause damage throughout the body. If you suspect that you have blood clots in the brain, immediate treatment will be necessary to avoid a life-threatening condition.
A blood clot in the brain can cause an ischemic stroke which is caused by an artery to the brain becoming blocked and starving a portion of the brain of oxygen and nutrients. A clot in the brain can also cause a buildup of cellular waste and carbon dioxide because the brain will be unable to clear this waste properly. This can cause the cells around the blockage to die, and the neurons in this portion of the brain to stop working, which can cause damage throughout the body. If you suspect that you have blood clots in the brain, immediate treatment will be necessary to avoid a life-threatening condition.
Causes of Blood Clot in the Brain
Head injuries or trauma to the brain, head and neck can cause these clots to form in the brain. Blood clots in the brain are caused when bleeding occurs between the skull and the brain. The body will form a clot to stop the bleeding, which will put pressure on the surrounding brain tissue. Trauma to the head can also cause blood clots formed outside of the brain to break loose and become lodged in the brain, which can cause an ischemic stroke.
Travelling clots from other parts of the body will travel to a blood vessel that leads to the brain, causing a blockage and then an embolic stroke or cerebral embolism. These travelling clots are more likely to cause damage to other parts of the body before they reach the brain.
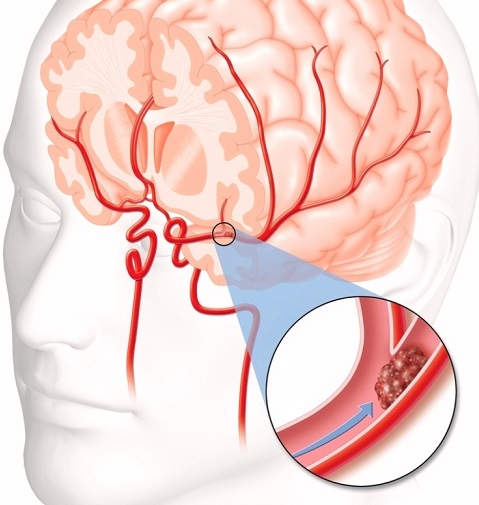
Narrowing or hardening of the arteries, commonly known as atherosclerosis, can increase someone's vulnerability to developing a clot in the brain. Hardened arteries are at risk of tearing as they pump blood, which can cause a clot to form in the damaged area so blood does not leak into the body. These clots can cut off blood flow to the narrowed artery, causing damage to the surrounding cells.
Inflammation of a superficial vein can also cause an increased risk of blood clots. If a vein is damaged due to a high trauma injury it can become inflamed. A bacterial infection in the vein can also cause this type of inflammation which will reduce blood flow to the surrounding area. These damaged areas will be at a higher risk for leaking, which will result in a blood clot. If the area is inflamed, then this blood clot could cut off the blood supply to the surrounding cells.
Women who use oral contraceptives may be at an increased risk for blood clotting. Women who have a history of blood clots, are over the age of 35 or smoke and continue to use contraceptives have an extremely high risk of developing blood clots which should be addressed by your doctor.
Symptoms of Blood Clot in the Brain
There are a variety of symptoms one may experience when having blood clots in brain, ranging from headaches to difficulty speaking, depression and ischemic attack.
- Headaches: Headaches associated with a blood clot will normally be found on one side of the head. These can be worsened by coughing or sneezing and can impair head movement or physical activity over time.

- Speaking difficulties: You may begin to slur your words or have difficulty speaking. This is especially prominent if you have a clot on the left side of the brain.
- Confusion: It may feel as though it takes longer to think, or your thinking capacity is not where it should be. You may feel confused or feel as though it takes longer than usual to understand things.
- Changes in personality: A blood clot can cause your personality to become altered from its usual state. You may suddenly feel very manic or normally energetic people can feel subdued.
- Dizziness: Bouts of dizziness may occur from time to time. This may be accompanied by temporary blindness.
- Depression: Those who suddenly develop depression are frequently checked for blood clot in the brain to ensure that all portions of the brain are getting the right amount of oxygen.
- Loss of coordination: You may find yourself unable to move with the same level of coordination that you are used to. The ability to transfer objects from one hand to the other may be mostly affected.
- Seizures: Seizures caused by a blood clot can last up to two minutes. Seizures that last longer may be a sign of a more serious condition.
- Paralysis: One side of your body may suddenly become paralyzed if you are suffering from a blood clot. The arm, leg and face will be mostly affected by this.
- Ischemic attack: This is also known as a "mini-stroke," which will cause dysfunction on one side of the body. If this condition escalates, it can become a full stroke.
Treatments for Blood Clot in the Brain
If you suspect you have a clot in your brain it is vital that you seek medical attention right away, including contacting emergency medical services if you believe you may be suffering from a stroke.
- An MRI or CT scan will need to be used to diagnose the presence of a clot and the condition which caused it to appear.
- Anti-coagulants such as aspirin can often be used to dissolve the clot. The patient may also be placed on an aspirin regimen to prevent the appearance of new clots. Do not take anti-coagulants if you are at risk for hypertension as this can interfere with your regular medication.
- Surgery: In some cases, a clot can be surgically removed from the brain. Arteries can also be opened and scraped clean of plaque to reduce the risk of additional injury. Patients at risk for developing additional clots may have a tissue plasminogen activator inserted in a vein. This will release clot-busting drugs directly to the brain to stop a stroke from occurring.
