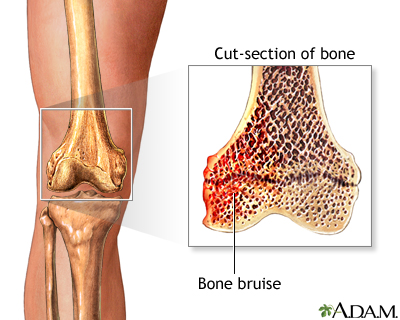
People frequently think of a black-and-blue mark on the skin when they hear the word "bruise." However, a bruise is a type of injury that can also involve the muscle or a bone. A bone bruise is an injury that involves the medullary part of the bone, which consists of fibrous tissue called trabeculae. Compared to a bone fracture where all trabeculae of a part of a bone are broken, only a few trabeculae are injured in a bone bruise, and it may therefore be described or considered as a stage before an actual fracture occurs.
This image (L) shows a knee bone that has been injured, and beside it is a longitudinal cut of the bone which shows the medullary part of the bone (red) that exhibits some broken bone fibers are bleeding.
A bone bruise commonly occurs in the knee bone, involving the long bone of the thigh or femur, but it can also occur in other parts of the body such as the wrist, heel, foot, or hipbone.
Kinds of Bone Bruise
Depending on the area of bone involvement, there are three kinds of bone bruises, which include a subperiosteal hematoma, an interosseous bruise, and a subchondral bruise.
- Subperiosteal hematoma - A bone has a thin covering called the periosteum, and a direct force can cause an injury with bleeding beneath this covering, resulting in a subperiosteal hematoma.
- Interosseous bruise - On the other hand, high compressive forces that are repetitively inflicted on a bone can cause bleeding inside the bone where the marrow is located, causing a bone bruise called interosseous bruising. This commonly occurs in the knees and ankles of professional basketball or football players.
- Subchondral bruise - Finally, there is the subchondral bruise which occurs between a cartilage and the bone beneath it, causing the cartilage to separate from the bone with bleeding in between.
Causes of Bone Bruise
A bone bruise usually results from either a direct and sudden force or from repetitive compressive forces that are not strong enough to break or fracture a bone. There are many ways one can suffer from a bone bruise.
- Sports injuries - Bone bruises are a common type of sports injuries, especially in those which involve a lot of falling or getting into hard contact with objects or other players. The knees and the ribs are commonly affected, and it is always advisable to wear proper sports gear to avoid these injuries.
- Twisting injuries - This can result in sprained ankles or knees, and these are usually accompanied by bone bruises. Twisting a joint causes the involved bones to collide with each other forcefully, leading to a bone bruise.
- High velocity trauma to a bone - In general, any type of direct impact or high velocity trauma to a bone brought about by an incident such as a car accident, a high fall, or a blunt force can result in a hematoma, a contusion, or a bruise to the bone affected.
Symptoms of Bone Bruise
Like most types of trauma, a bone bruise is characterized by pain and swelling. However, the pain involved tends to be more severe and lasts longer than a soft tissue trauma. The swelling may be seen around the soft tissue surrounding the bone, such as the skin and muscles, and may be accompanied by discoloration. When a bone bruise is adjacent to a joint, blood and fluids can spread to the joint, causing it to swell.
A bone bruise may cause minimal damage to a bone which may be detected with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) but not by plain x-rays.
Treatments for Bone Bruise
After a traumatic injury, it is best to rule out a fracture by consulting a doctor who may request tests to be done. When a bone bruise is diagnosed with an MRI, one should rest the involved bone or joint and avoid any type of stress that could impede the healing process.
Immediately apply an icepack or ice wrapped in thin cloth over the injured area to prevent excessive swelling and pain.
One can also take anti-inflammatory medications to reduce severe inflammation and pain, which can last for more than a few weeks to a month. These may include over-the-counter drugs non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) like ibuprofen (Motrin), diclofenac (Voltaren), or piroxicam (Feldene). However, it is important to take these drugs at the proper dose, preferably with food, to avoid common side effects like gastrointestinal disturbances.
Avoid placing more stress on the bruised bone area to allow adequate healing. A bone bruise heals more slowly than a soft tissue damage. To support and protect a bone near a joint from further trauma, it is advisable to wear a brace, such as a knee brace.
Experts also advise against using tobacco or nicotine, which can delay the healing process, since they constrict blood vessels, thus reducing blood flow to the area.