 Prostate gland enlargement is a common problem encountered in old age by men. This problem is given the medical name of benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH. The most common symptom of this problem is having difficulty in urination which is usually very mild. If treatment is not started, there is a chance the condition might improve on its own. However, if the symptoms worsen, then taking medications or even surgery becomes necessary.
Prostate gland enlargement is a common problem encountered in old age by men. This problem is given the medical name of benign prostatic hyperplasia or BPH. The most common symptom of this problem is having difficulty in urination which is usually very mild. If treatment is not started, there is a chance the condition might improve on its own. However, if the symptoms worsen, then taking medications or even surgery becomes necessary.
What Causes Enlarged Prostate Gland?
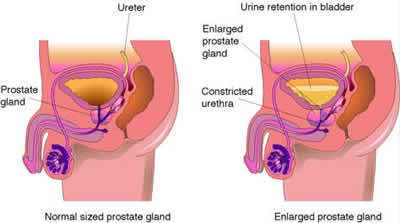
The location of the prostate gland is such that it lies underneath the bladder. Urethra or the tube responsible for taking the urine out of the bladder to your penis has to pass through the middle of the prostate gland. Now if the prostate gets enlarged, the flow of the urine gets blocked.
The growth of the prostate never ceases to stop in most of the men. Because of this continuous growth, the prostate can become large enough in some men that it might start blocking the flow of urine or cause other urinary complications.
Although there is no evidence present as to the reason for the enlargement of the prostate, it is considered that the imbalance of the sexual hormones in older men might be the reason for it.
Risk Factors of Enlarged Prostate Gland
The following are some of the factors that increase your chances of having an enlarged prostate gland.
|
Risk Factors |
Description |
|
Aging |
Men who are in their 40s do not experience symptoms caused by prostate gland enlargement. Almost 1 in 3 patients start feeling the severity of the symptoms when they reach age of 60 years while around 50% of them start exhibiting the signs in their 80s. |
|
Family history |
People having a family history of this problem are more likely to develop it. The risk increases if you brother or father suffers from prostate enlargement. |
|
Ethnic background |
Asian men are far less likely to develop prostate enlargement than black and white men. The symptoms of the problem begin to show earlier in black men as opposed to white men. |
|
Diabetes and heart disease |
Studies have revealed that using beta blockers, having a heart condition or suffering from diabetes can elevate your chances of getting BPH. |
|
Weight and lifestyle |
Doing regular exercise can decrease your chances of getting this problem while obesity can increase it. |
What Are the Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate Gland?
Symptoms
Lower urinary tract symptoms or LUTS is the name given to the symptoms of prostate gland enlargement. However, LUTS can occur because of other diseases and disorders as well.
Enlargement of the prostate can narrow down the urethra’s path, causing an obstruction in urine flow. The following symptoms might result from this:
- Poor stream. Having a weak urine flow, increasing the time period for emptying your bladder.
- Hesitancy. Having to wait in the toilet for sometime before flow of urine begins.
- Dribbling. The urine flow ends in a dribble which continues on for a lengthy time period.
- Poor emptying. Having the feeling that the bladder has not been totally emptied.
Irritability of the bladder is also sometimes caused by the enlargement of the prostate gland which might lead to:
- Frequency. This involveshaving to pass urine at regular intervals much higher than normal. If this happens at night then this symptom in known as nocturia and it might wake you up many times during your sleep.
- Urgency. This involves having to run to the toilet when you are feeling the need to pass urine.
In the beginning the symptoms of BPH are very mild and slowly with the passage of time, they become more pronounced and start affecting your urination. In some cases, there is a chance of complications as well.
Important Notes:
- It is not uncommon for a man to not experience any symptoms even though he has an enlarged prostate. Do remember that the obstruction caused by the prostate will determine the severity of your symptoms and not the size of your prostate.
- Enlarged prostate is not the only cause of urinary problems in men. For instance incontinence, having blood in urine or experiencing pain when urinating can be caused by a kidney or bladder infection.
Complications of Enlarged Prostate Gland
Enlargement of the prostate gland can cause complication like:
- Urinary retention. People who suffer from urinary retention might have to use a catheter to drain the urine present in their bladder. Sometimes even surgery is needed to get the patient relief from the urinary retention.
- UTIs (Urinary tract infections). If you can’t empty your bladder, you will run the risk of having an infection in your urinary tract. If the infections occur repeatedly then you would have to surgically remove the prostate that has been blocking the urethra.
- Bladder stones. Not being able to empty the bladder can lead to bladder stones. These stones can result in bladder irritation, blocking of urine flow, infections and bloody urine.
- Bladder damage. Weakening or stretching of the bladder can occur if the bladder is not emptied during urination. Because of this the muscular wall that helps the bladder to contract loses its contracting ability and the bladder does not get emptied when you urinate.
- Kidney damage.Urinary retention can put undue pressure on the kidneys and might cause damage to them. It can also aid in the passing of the bladder infections to find their way through to the kidneys.
The chances of contracting prostate cancer do not rise because of an enlarged prostate gland.
When to See a Doctor
If you find that you are not urinating properly or not emptying your bladder entirely when urinating then you must immediately consult with your doctor. Give a detailed account of all of your symptoms to your doctor without leaving anything out.
Ask your doctor if any of the drugs that you are taking are responsible for your urinary problems. For instance diuretics, antidepressants, sedatives and antihistamines might affect the urinary system. The doctor will make any changes in the drugs if he feels necessary but you should not make the changes yourself. If you are doing anything at home to alleviate your symptoms but they are not having any effect then you must tell your doctor about them.
Video: the enlarged prostate explained by a urologist:
