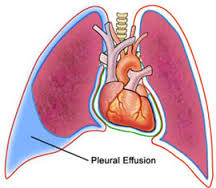
 Known also as fluid in the chest, pleural fluid or fluid on the lung, a pleural effusion is fluid building up on the pleural space. This is an area between tissue layers which line the chest cavity and lungs. It could also be referred to as pulmonary effusion or just effusion. The kind of fluid which forms a pleural effusion could be categorized as either transudate or exudate. Usually, the more serious and difficult to treat are exudative pleural effusion.
Known also as fluid in the chest, pleural fluid or fluid on the lung, a pleural effusion is fluid building up on the pleural space. This is an area between tissue layers which line the chest cavity and lungs. It could also be referred to as pulmonary effusion or just effusion. The kind of fluid which forms a pleural effusion could be categorized as either transudate or exudate. Usually, the more serious and difficult to treat are exudative pleural effusion.
Causes of Pleural Effusion
Your body makes pleural fluid to lubricate the surfaces of the pleura in small amounts. This is a thin tissue which lines the chest cavity and surrounds the lungs. An excessive and abnormal buildup of the fluid is pleural effusion.
The two types and their causes are:
- Exudative effusion is from blood vessels or lymph nodes being blocked, and also lung injury, inflammation and tumors.
- Transudative effusion is the result of leaking fluid into the pleural space. It is from low blood protein count or increased pressure in the blood vessels. The most common cause of this is congestive heart failure.
Symptoms of Pleural Effusion
Many times, no symptoms are seen. More than likely, symptoms will appear when a pleural effusion is moderately or largely sized, or if inflammation is there. Symptoms can include:
- Chest pain, especially when breathing in deep (pleuritic or pleurisy pain)
- Shortness of breath
- Fever
- Cough
Other symptoms include hiccups, malaise, rapid breathing, etc.
Complications could include:
- Infection which turns into an abscess, known as an empyema; it will have to be drained out via a chest tube
- Lung damage
- Air inside the chest cavity (pneumothorax) after thoracentesis
Diagnosis of Pleural Effusions
Your doctor may diagnose after a physical examination and your symptoms. They could use auscultation, which is listening with a stethoscope, percussion or tapping on your chest, plus other methods when this condition is suspected.
Most of the time, pleural effusions are found on imaging tests. The usual tests that will identify pleural effusions are:
- Chest X-ray film: Many times, the first step in diagnosing is plain X-ray films. They will show up on chest X-rays as a white space at the bottom of the lung. If the condition is likely, another X-ray will be taken while you lie on your side. These are called decubitus X-ray films, and can show if the fluid flows in the chest freely.
- Ultrasound: Here a probe is put against your skin which reflects high-energy sound waves off chest structures, making images on a screen. This test can help guide drainage and also identify if the pleural effusions are free-flowing. After the condition is identified, a sample of fluid is normally taken to figure out what the character of the effusion is and how serious it is. During thoracentesis, your doctor will insert a needle and catheter between your ribs into the pleural space. A bit of fluid is taken out for testing, and a large amount can be removed at the same time to relieve symptoms.
- Computed tomography (CT scan): This involves taking numerous X-rays quickly, and then a computer constructing the images of the inside of the chest. Compared with chest X-rays, CT scans make more detailed information of pleural effusions and other abnormalities of the lungs.
Treatments for Pleural Effusion
The end goal of treatment is to:
- Stop fluid from building up again
- Take out the fluid
- Find and treat the cause of the buildup of fluid
Taking out the fluid, or thoracentesis, could be done if there is a lot of fluid and it is leading to pressure in the chest, shortness of breath or other breathing problems like low oxygen. Taking out the fluid lets the lung expand, therefore making it easier to breathe.
The cause for the fluid buildup has to be treated as well.If congestive heart failure is the reason, you could receive diuretics, or water pills, plus other medications for heart failure.
When infection is the cause, pleural effusion antibiotics are used for treatment.For people with infection or cancer, the effusion many times will be treated with a chest tube so the fluid can drain for several days.
Small tubes can sometimes be left in the pleural cavity for a longer time to drain fluids. Sometimes, the following could be done:
- Putting medications in the chest which stops fluid from building up again once it is drained
- chemotherapy
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
In a lot of cases, however, unless treatment can be given for the underlying cause, an effusion will probably return in a few weeks. When symptoms become troublesome, repeated draining of the fluid is an option.
What You Should Know About Asbestos and Its Harms
A group of minerals with thin microscopic fibers is known as asbestos. Since these fibers are resistant to fire and heat, and chemicals and they don’t conduct electricity, asbestos has beenwidely used in the automotive, construction and other industries.
When products containing asbestos are disturbed, the tiny fibers are put out into the air. They can become trapped in the lung for many years when they are breathed in. over time, these fibers can add up and lead to serious health problems, which include:
- Lung cancer
- Asbestosis – this is an inflammatory condition of the lungs which can cause coughing, shortness of breath and in the long run scarring of the lungs that makes breathing difficult.
- Mesothelioma – a rare cancer which affects the lung lining, abdomen or the cavity of the chest.
- Other lung problems – this includes pleural plaques, or changes in the membranes that surround the lungs, thickening of the membranes which surround the lungs, and pleural effusions.
Studies have suggested that an association exists between asbestos exposure and other cancers, which includes gastrointestinal tract cancers, kidney, throat, brain, voice box, bladder, and gallbladder.
Causes and Risks of Asbestos Exposure
Exposure to asbestos can happen in the home, workplace or community. It was used in many products, being commercial mined since the 1800s. Things such as car clutch pads and brake shoes, building materials like floor and ceiling tiles, coatings, paints and adhesives, plastics and garden products with vermiculite may all contain Asbestos. Because of health concerns and federal regulations however, asbestos is much less widely used than even a few decades ago.
Most cases of asbestos poisoning happen in workers dealing with asbestos. Some family members of these workers who were heavily exposed have a higher risk however due to the fibers being brought home on skin, clothing and hair. Mesothelioma cases have been seen in people living close to the mines as well.
