This condition can be caused by increased melanin or melanosis within the outer layer of the skin or deposited in the deeper layer of the skin.
Some conditions can cause post inflammatory hyperpigmentation:
- Inflammatory skin reaction, such as dermatitis, acne or psoriasis
- Skin infections caused by fungi, viruses, bacteria or parasites
- Reactions to medications, such as drug eruptions
- Trauma, such as abrasion or thermal burn
- Phototoxic eruptions, such as plant dermatitis
Inflammatory response of the epidermis to trauma or disease results in the release of certain substances, such as prostaglandins, leukotrienes, and other. These substances affect the activity of immune cells and the melanocytes (pigment producing cells). An increased number of these cells produce more skin pigment melanin, which is transferred to surrounding skin cells.
What Does Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation Look Like?
It appears as a flat area of discoloration on the skin. The color of this discoloration ranges from pink to purple, red, brown or black, depending on the type and tone of your skin and the depth of discoloration.
PIH develops when a rash, a wound, pimple or other conditions cause skin inflammation. This triggers your skin to produce more melanin. The excess of melanin darkens the wounded area. The discoloration remains after the affected area has healed.
PIH is very common in those who suffer from acne. It can affect all skin types, but it is more common in darker skin types. PIH affects men and women equally. Note that this skin condition is not a true scar.
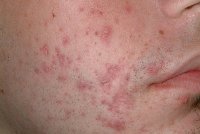
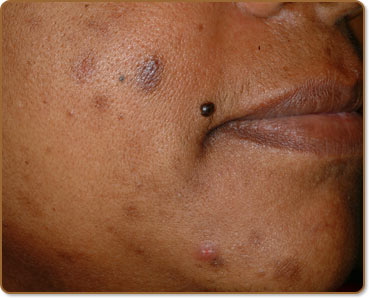
What to Do About Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
It may resolve without any additional treatment. The primary care includes:
- Daily use of sunscreen with high protection against UVA and UVB rays and avoidance of sun exposure
- Treatment of the root cause
- Use vitamins and natural ingredients to fade the dark spots.
Home Remedies for Acne Scars and Hyperpigmentation (Lemon Juice for Acne):
Other treatment options can help to reduce the PIH faster. These options include:
- Combination of alpha and beta hydroxyl acids, Vitamin A, Vitamin C and other treatments to exfoliate the sun.
- Topical application of retinoids (such as tretinoin or tazarotene) are effective for those who suffer from acne, as they treat both acne and discolorations.
- Application of glycolic acid can help to lighten the affected areas. Glycolic acid is available in creams, cleansers, gels and other skin care products. Higher concentrations of this acid are available with a doctor’s prescription.
- Combination of retinaldehyde, glycolic acid and the peroxidase inhibitor methimazole, which reduces the production of melanin.
- Products containing N-acetyl glucosamine and niacinamide, such as Olay® Definity
- Application of hydroquinone cream (1%-4%) is a popular treatment for post inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Hydroquinone creams often contain such lightening ingredients as glycolic acid, tretinoin, Vitamin C or kojic acid. Combined creams are usually more effective.
- Azelaic acid is available by prescription only. This acid decreases the inflammation and speeds up cell turnover rates.
Topical application of some treatments may cause side reactions. There are some safety concerns about hydroquinone. Some studies show that is has cancer-causing potential. Topical retinoids can cause irritation and dryness, resulting in an increased hyperpigmentation.
Professional Treatment
A number of oral and topical agents are currently under investigation. Individuals with post inflammatory discoloration should be informed that hyperpigmentation can be slow to reduce, even with treatment. Epidermal pigmentation can persist for a year, dermal pigmentation can remain for years. More persistent cases of skin discoloration may be treated at your dermatologist’s office or skin spas. A number of treatment sessions may be required to fade discoloration.
When to Seek Medical Care
See your doctor if it‘s distressing to you, if you suffer from a chronic skin condition resulting in the darkening or if you notice a general unexpected and unexplained change in your skin color.
